Japanese tech companies hiring software developers.
21 Feb 2024
How to Write an Efficient CV for Job Application in Japan
Differences between CV and Resume in Japan
Understanding the distinction between a 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV) and a 履歴書 (Rirekisho, resume) is crucial for job seekers in Japan, as each serves a different purpose in the application process.
職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV)
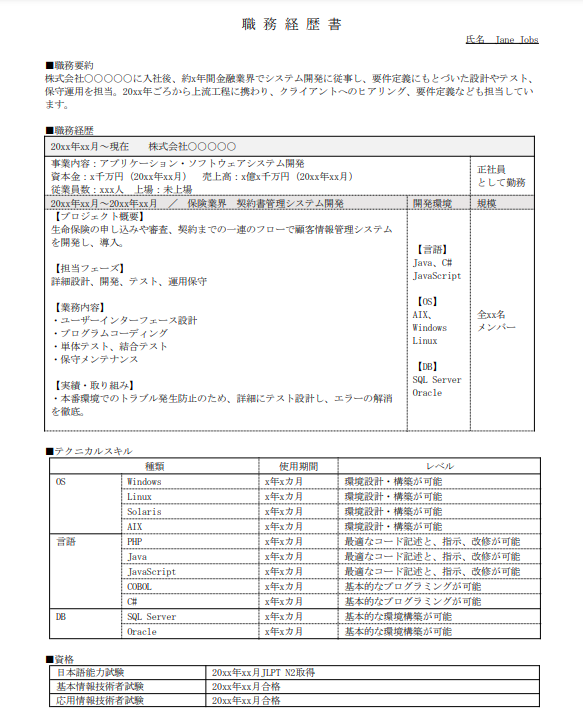
- Purpose: Focuses on detailing your career history, skills, and achievements. It's primarily used by individuals with work experience looking to change jobs, offering a comprehensive view of their professional background.
- Content: Includes a detailed account of previous positions, responsibilities, accomplishments, and the specific skills utilized in each role. It's an opportunity to showcase how your experiences align with the job you're applying for.
履歴書 (Rirekisho, Resume)
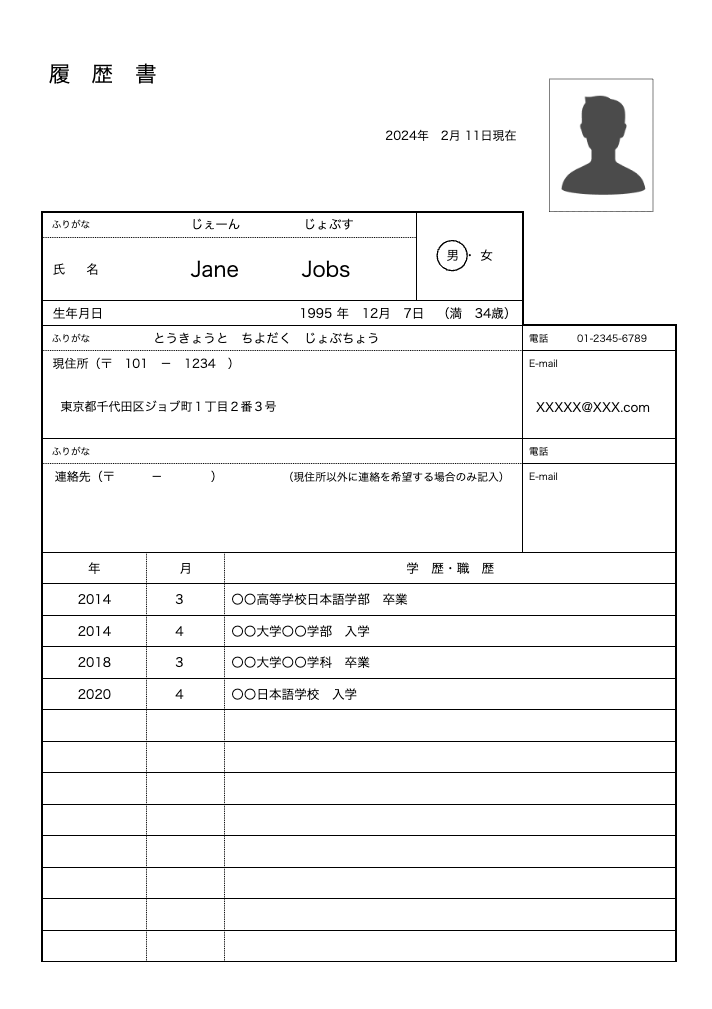
- Purpose: A mandatory document for all job applications, regardless of whether you're a new graduate or an experienced professional. It provides a snapshot of your personal and professional background.
- Content: Contains basic personal information, educational background, work history, and qualifications. Some companies may request an "エントリーシート" (Entry Sheet) for new graduates, which is a customized form with unique questions designed to assess candidates more personally.
See Also: How to Write a great Japanese Resume (Rirekisyo)
See Also: How to Write an English Resume for Japanese Companies
Key Differences
- Usage: The Resume (Rirekisho) is used universally across all job applications in Japan, while the Shokumukeirekisho is specifically for those with prior work experience searching for the next job.
- Detail: The CV (Shokumukeirekisho) offers more space to elaborate on professional experiences and skills, whereas the Rirekisho is more concise, focusing on basic information and a brief employment history.
- Customization: The CV (Shokumukeirekisho) allows for greater customization to match the specific job and company, emphasizing relevant experiences and skills. The Resume (Rirekisho) follows a more standardized format, with less room for personalization.
Understanding these differences enables job seekers to prepare their applications more effectively, ensuring that they provide the most relevant and impactful information to potential employers in Japan.
Should Your CV Be Written in Japanese?

When applying to Japanese companies, the language used in your 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV) plays a significant role in your application's success. Here's what to consider when deciding between Japanese or English for your CV.
The Case for Japanese
- Default Expectation: For most positions, especially in traditional Japanese companies, a CV written in Japanese is the standard expectation.
- Accessibility: A Japanese CV ensures that all hiring personnel, who may not be proficient in English, can fully understand your qualifications and experience.
When English Might Be Appropriate
- International Firms: For roles in international companies or organizations where English is the working language, an English CV may be acceptable or even preferred.
- Specific Instructions: If a job listing explicitly states that applications can be in English, it's safe to submit your CV in English. This is often the case for positions requiring high English proficiency.
Best Practices
- Inquire When in Doubt: If you're unsure about the company's preference, it's advisable to contact their HR department for clarification. This can also demonstrate your proactive approach and attention to detail.
- Consider Your Language Proficiency: If your proficiency in Japanese is not strong, and the company accepts English CVs, it might be better to submit an English CV to ensure clarity and accuracy in your application.
While a Japanese CV is generally preferred when applying to companies in Japan, there are exceptions based on the company's culture and the specific job requirements. Assessing each situation carefully and choosing the appropriate language for your CV can significantly impact the impression you make on potential employers.
What Japanese Employers Look for in a CV

When reviewing a 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV), Japanese employers focus on several key aspects to assess a candidate's suitability for the position. Understanding these focal points can help you tailor your CV to better align with what potential employers are seeking.
Key Aspects of Evaluation
- Past Roles and Skills: Employers want to understand the nature of your previous positions and the skills you've developed. This includes the scope of your responsibilities and any specialized expertise you possess.
- Achievements: Concrete achievements, especially those quantifiable with numbers, are highly valued. They provide clear evidence of your impact in previous roles.
- Management Experience: For roles involving leadership, your experience in managing teams or projects is crucial. It indicates your ability to lead and coordinate effectively.
- Reason for Changing Jobs: Employers look for positive, forward-looking reasons for your job change. They prefer candidates who are motivated by growth and new challenges rather than those leaving a position for negative reasons.
Crafting Your CV with These Points in Mind
To make your CV stand out:
- Highlight Your Achievements: Use specific examples and numbers to demonstrate your accomplishments in past roles.
- Detail Your Skills: Clearly list the skills you've acquired, focusing on those relevant to the job you're applying for.
- Explain Your Career Progression: Offer a narrative that shows a logical progression in your career, leading up to why you're seeking this new opportunity.
- Be Positive About Career Moves: Frame your reasons for changing jobs in a positive light, focusing on what you hope to achieve in the future.
By emphasizing these elements in your CV, you signal to Japanese employers that you not only have the requisite experience and skills but also the right mindset and motivation for the job.
Preparing to Write Your CV for Job Application in Japan

Before you start writing your 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV), there are essential steps to ensure your document is as effective and tailored as possible.
Here's what you need to do in preparation:
Inventory Your Career and Skills
- Reflect on Your Achievements: List out all significant achievements in your career, focusing on those that can be quantified or clearly demonstrate your impact in previous roles.
- Skill Assessment: Make a comprehensive list of your skills, both soft and hard. Include languages, technical skills, and any other competencies relevant to the job you're applying for.
Tailor Your Points for Each Company
- Research the Company: Understand the company's culture, values, and the specific requirements of the job. This will help you decide which aspects of your career and skills to highlight.
- Customize Your Approach: Based on your research, tailor your CV to align with the company's needs and the role's demands. Choose achievements and skills that best match what they're looking for.
Essential Sections and Format for Your CV

When crafting a 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV) for job applications in Japan, including specific sections and adhering to a professional format is crucial. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components and how to organize them:
Professional Summary (職務要約, Shokumu Youyaku)

- Purpose: Provides a concise overview of your career highlights and key strengths.
- Content: Limit this section to 6-7 lines, focusing on significant achievements and skills, ideally quantified with numbers to demonstrate impact.
Job History (職務経歴, Shokumu Keireki)

- Detailing Your Career: List your previous positions, starting with the most recent. Include the company name, your role, period of employment, main responsibilities, and notable accomplishments.
- Format: Each entry should clearly outline your contributions and the skills you applied, highlighting how each experience is relevant to the job you’re applying for.
Certifications (資格, Shikaku)

- Listing Qualifications: Mention any professional certifications or qualifications that enhance your candidacy, specifying the issuing organization and the date obtained.
Skills (スキル, Sukiru)
- Showcasing Your Abilities: Detail both soft and hard skills relevant to the position. For technical roles, include specific technologies or methodologies you’re proficient in.
Self-Promotion (自己PR, Jiko PR)
- Highlighting Your Strengths: Use this section to present 2-3 of your core strengths with examples or brief stories that illustrate these attributes effectively.
- Structure: Start with a clear statement of your strength, followed by evidence or an example that supports it. Repeat this structure for each strength you wish to highlight.
Formatting Tips
- Clarity and Professionalism: Ensure your CV is easy to read, with a clean layout and professional font. Use bullet points for lists and keep margins consistent.
- Language Proficiency: If you’re bilingual, clearly state your proficiency levels, especially in Japanese and English, as this can be a significant advantage.
Key Points for a Successful CV

Crafting a successful 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV) for the Japanese job market involves more than just listing your experiences and skills. Here are three critical points to ensure your CV stands out and positively impacts hiring managers.
Conciseness and Clarity
- Be Succinct: Your CV should be concise yet informative. Avoid unnecessary details that don’t contribute to your candidacy for the specific role.
- Use Numbers: Wherever possible, quantify your achievements. Numbers provide a clear measure of your impact and success in previous roles.
Clear Job History
- Detail Your Roles: Clearly outline your responsibilities and achievements in each position. This helps employers understand the scope of your experience and the value you brought to past roles.
- Chronological Order: Present your job history in reverse chronological order, ensuring a logical flow and making it easy for readers to follow your career progression.
Effective Self-Promotion
- Highlight Your Strengths: Use the self-promotion section to focus on your unique strengths. Back up your claims with concrete examples or brief anecdotes that demonstrate these qualities in action.
- Tailor to the Role: Customize this section to align with the job you’re applying for, emphasizing the skills and experiences that make you an ideal candidate.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Applicants from abroad often make mistakes such as:
- Failing to Tailor the CV: Each application should be customized to the job and company, highlighting the most relevant experiences and skills.
- Overlooking the Importance of Language Skills: Especially in Japan, indicating your proficiency in Japanese (and English, if applicable) is crucial.
- Neglecting the Format: Japanese employers expect a certain level of formality and structure in CVs. Adhering to traditional formats and ensuring your CV is neatly organized can make a significant difference.
A successful CV for the Japanese job market is one that effectively communicates your career achievements, skills, and potential value to the employer in a clear, concise manner. By focusing on these key points and avoiding common pitfalls, you can create a compelling CV that captures the attention of hiring managers and advances your job application.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Your CV

When crafting a 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV) for the Japanese job market, especially as a foreign applicant, there are common pitfalls you should be aware of to ensure your application is received positively. Avoiding these mistakes can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your CV.
Overgeneralization
Avoid being too vague about your responsibilities and achievements. Instead of general statements like "managed a team," specify what you managed the team to achieve, how many team members there were, and the impact of your leadership.
Ignoring Japanese Business Etiquette
Japan values humility and teamwork. Highlighting too aggressively individual achievements over team contributions can be perceived negatively. Balance is crucial; showcase your achievements within the context of contributing to team goals.
Language Proficiency Overestimation
Misrepresenting your language skills, especially your proficiency in Japanese, can lead to misunderstandings and challenges in the recruitment process. Be honest about your language levels to set clear expectations.
Neglecting the Importance of Format and Presentation
Japanese CVs have a specific format that is expected to be followed. Disregarding these formatting guidelines can signal a lack of attention to detail or unfamiliarity with Japanese business practices.
Failure to Tailor the CV
Submitting the same CV for multiple job applications without tailoring it to highlight the most relevant skills and experiences for each position is a common mistake. Customization shows you've researched the company and understand the role.
Avoiding these common mistakes in your 職務経歴書 can make a substantial difference in how your application is perceived by potential employers in Japan. By focusing on specificity, cultural sensitivity, accurate language representation, proper formatting, and CV customization, you can present a strong, appealing application that aligns with Japanese business etiquette and job market expectations.
Is Handwriting Your CV Necessary?

In the context of Japan's job market, the question of whether to handwrite your 職務経歴書 (Shokumukeirekisho, CV) or to create it digitally is significant, given the traditional emphasis on handwritten documents. However, the norms are evolving, and understanding current expectations is crucial.
The Tradition of Handwriting in Japan
Historically, handwriting documents, including CVs, was seen as a demonstration of one’s personal effort and attention to detail. It was believed to offer insights into an applicant's personality and work ethic.
However, in recent years, there's been a noticeable shift towards digital submissions. The reasons include:
- Efficiency: Digital documents are easier to store, organize, and review.
- Clarity: Typed documents offer uniformity and readability, ensuring that information is easily accessible.
- Modern Work Environment: As companies modernize, the acceptance of digital documents aligns with broader shifts towards digital workflows.
Current Best Practices
- Follow Company Guidelines: Always adhere to the application instructions provided by the company. If they specify a preference for handwritten or digital documents, follow their lead.
- Consider the Role and Industry: In creative industries or roles where personal touch is valued, a handwritten CV might still be appreciated. Conversely, for tech-focused or international companies, digital is likely preferred.
- When in Doubt, Go Digital: Unless specifically instructed otherwise, submitting a digital CV is generally acceptable and often expected. It allows for easier revision and ensures your information is presented clearly.

